property()
Here’s how to use property() function.
f. property()
Description:
Retrieve property value from the property file.
Syntax:
f.property(p)
Note:
The function retrieves property p from property file f and return.
Parameter:
|
f |
A file object. |
|
p |
Property name; the function returns a table sequence composed of all properties if it is omitted. |
Option:
|
@v |
Read a property value and parse it as what it is; by default, return the value as a string. |
Return value:
Value/Table sequence
Example:
A regular scenario:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
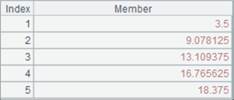
=file("E://test.property").property("color") |
Below is content of test.property:
Return “red” as the result: |
|
2 |
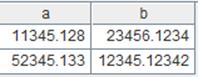
=file("E://test.property").property() |
|
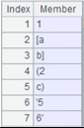
Scenario of reading color scheme for a graph:
The color scheme file is [installation directory]\esProc\classes\config\chartcolor.properties. A color scheme format is color scheme name=[color1,color2,….]:
Set colourful8 as the color scheme for the column graph:
Note:
To use the color schemes in plotting a graph, make sure that the class path can be loaded onto the config directory. esProc default design is that the config directory is already put into [installation directory]\esProc\classes. To view the effects of color schemes on server side, users need to create a config folder in the service’s [applicaton root directory]\WEB-INF\classes unless there’s already a config folder there and copy the color scheme file chartcolor.properties under it.
Related function:
xs.property()
Description:
Read property values from node strings.
Syntax:
xs.property(n,v)
Note:
The function retrieves value of property named n from node string xs. Set n’s value as v if parameter v is present, and delete n if v is absent. Return a table sequence made up of all properties when no parameters exist.
Parameter:
|
xs |
Node strings, whose format is “name1=value1 name2=value2...” . |
|
n |
Node string name. |
|
v |
Null or a string. |
Option:
|
@c |
Separate node strings by commas or semicolons; use spaces by default. |
|
@j |
Use colons to separate node string name and its value; use the equal sign by default |
|
@q |
Enclose values by double quotation marks. |
|
@v |
Read the string and then parse it into value; return a sequence by default. |
Return value:
A single value/Sequence
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
color=red size=20 price=500 |
|
|
2 |
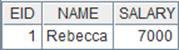
=A1.property("color","blue") |
Change the value of node string named “color” into “blue” . |
|
3 |
=A1.property@q("size") |
Enclose the value with double quotation marks. |
|
4 |
=A1.property@v() |
Use @v option to read the string first and then parse it into a value; as parameters are absent, the function returns a sequence of all properties.
|
|
5 |
color:red;size:20;price:500 |
|
|
6 |
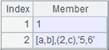
=A5.property@cj("color",) |
Use @cj options to retrieve property vlaues. Use semicolon to separate node strings, and use colon to separate node string name and node string value. Since parameter n is “color” and the value of parameter v is null, delete the node from the node strings. Below is the result returned:
|