keys()
Here’s how to use keys() function.
T.k eys()
Description:
Set key for a table sequence.
Syntax:
T.keys(Ki,…)
Note:
The function sets Ki,… as the key of the table sequence T. When parameter Ki is absent, delete T’s key. A T.create() operation will copy the key at the same time.
Parameter:
|
T |
A table sequence. |
|
Ki |
The key of table sequence T. |
Option:
|
@t(Ki,…,KT) |
Set the last parameter KT as the time key, and make all other parameters the base keys. |
Return value:
Table sequence
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=demo.query("select EID,NAME,DEPT,SALARY,HIREDATE from EMPLOYEE order by EID asc,DEPT asc") |
Return a table sequence:
|
|
2 |
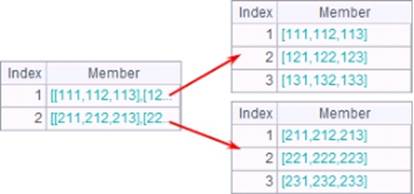
=A1.keys(EID,DEPT) |
Set EID field and DEPT field as A1’s key:
In a esProc result set, a
field whose name is marked by |
|
3 |
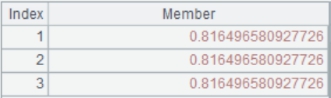
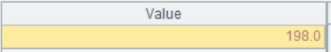
=A1(1).key() |
Get base key values in table A1’s first record and return [1, "R&D"]. |
|
4 |
=A1.keys() |
Remove the key as the parameter is absent. |
|
5 |
=A1(1).key() |
null. |
|
6 |
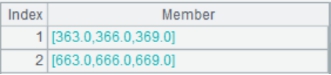
=A1.keys@t(EID,DEPT,HIREDATE) |
Set EID and DEPT as A1’s base keys and HIREDATE as the time key:
|
|
7 |
=A1.create() |
Copy table A1’s structure as well as its key. |
|
8 |
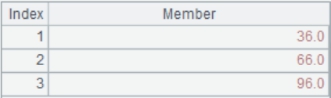
=A7.insert(0,1,"Jack","HR",3000,date("2022-03-09")) |
Add a record to table A7:
|
|
9 |
=A7(1).key() |
base keyGet base key values in table A7’s first record: [1,"HR"] |
Related functions:
T.keys( Ki,… )
Description:
Set key(s) for an in-memory table.
Syntax:
T.keys(Ki,…)
Note:
The function sets Ki,…as the key of in-memory table T.
Parameter:
|
Ki |
Key name; can be one or multiple keys; delete all keys of an in-memory table when the parameter is absent. |
|
T |
An in-memory table. |
Optios:
|
@t(Ki,…,KT) |
Set the last parameter KT as the time key and all other key fields constitute the base key. |
Return value:
In-memory table
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=demo.cursor("select EID,NAME,GENDER from EMPLOYEE where EID<10") |
Return cursor of the retrieved data. |
|
2 |
=A1.memory() |
Return an in-memory table.
|
|
3 |
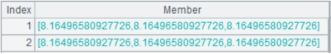
=A2.keys(EID,NAME) |
Set EID and NAME as the in-memory table’s keys:
In a esProc result set, a field whose name is marked
by |
|
4 |
=A3(1).key() |
Get base key values of the in-memory table’s first record and return [1, " Rebecca"]. |
|
5 |
=A2.keys() |
Delete all keys of the in-memory table as the parameter is absent. |
|
6 |
=A3(1).key() |
Get base key values of the in-memory table’s first record and return null. |
|
7 |
=demo.cursor("select EID,NAME,HIREDATE from employee").memory() |
Return an in-memory table. |
|
8 |
=A7.keys@t(EID,HIREDATE) |
Set EID as the base key and HIREDATE as the time key in A7’s in-memory table:
|
|
9 |
=A7(1).key() |
Get base key values of the in-memory table’s first record and return 1. |
T.keys@i(Ki, … ;n)
Description:
Set primary key for a table sequence or an in-memory table and create index for them.
Syntax:
T.keys@i(Ki,…;n)
Note:
The function sets Ki,... as primary key of table sequence/in-memory table T and, in the meantime, creates an index on the key.
Create hash index when the function only works with @i option.
Parameter:
|
Ki |
Primary key, which can be one or multiple; delete all keys of T when this parameter is absent. |
|
T |
A table sequence/in-memory table. |
|
n |
An integer greater than 1, which is length of the hash table; its default length is the table length; cannot create a serial byte index when this parameter is present. |
Option:
|
@s |
Create a serial byte index for a serial byte primary key; omit parameter n when using this option. |
|
@m |
Enable parallel processing to create the index. |
|
@t |
Set the last Ki parameter as the time key and create index on the base key. |
|
@n |
Create a sequence number key. |
Return value:
Table sequence/In-memory table
Example:
Set key for a table sequence and create hash index:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=demo.query("select EID,NAME,DEPT,SALARY from EMPLOYEE") |
|
|
2 |
=A1.keys@i(EID,DEPT;5) |
Set EID and DEPT as the key of A1’s table sequence and create a hash index whose size is 5. |
|
3 |
=A1.keys@im(EID,NAME) |
Create index using parallel processing. |
Set key for an in-memory table and create hash index:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=demo.cursor("select EID,NAME,DEPT,SALARY,HIREDATE from EMPLOYEE").memory() |
Generate an in-memory table based on a cursor. |
|
2 |
=A1.keys@i(EID,DEPT;5) |
Set EID and DEPT as the key of A1’s in-memory table and create a hash index whose size is 5. |
Create indexes of others types:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=demo.query("select EID,NAME,DEPT,SALARY,HIREDATE from EMPLOYEE") |
|
|
2 |
=A1.keys@in(EID) |
Set EID as the key of A1’s table sequence and create an sequence number index. |
|
3 |
=A1.keys@it(EID,HIREDATE) |
Set EID as base key and HIREDATE as time key for A1’s table sequence, and create index on the time key. |
|
4 |
=A1.keys() |
Delete all keys of A1’s table sequence as parameters are absent. |
|
5 |
=A1.derive(k(EID:3):PID) |
Add a serial byte field to the table sequence. |
|
6 |
=A5.keys@is(PID) |
Set PID as the key of A5’s table sequence and create a serial byte index. |