xlsimport()
Here’s how to use xlsimport() function.
f. xlsimport()
Description:
Retrieve contents of an Excel file and return them as a table sequence.
Syntax:
f.xlsimport(Fi,…;s,b:e;p)
Note:
The function retrieves field Fi from row b to row e from Excel file f’s sheet s and returns them as a table sequence. Retrieve data from the first row to the last one when both parameter b and parameter e are absent.
Parameter:
|
f |
An Excel file. |
|
Fi |
To-be-retrieved fields; by default, all fields will be retrieved. The sign # is used to represent a field with a sequence number. |
|
s |
Sheet name or sheet number; use the first sheet when omitted. |
|
b |
The starting row; if omitted, retrieve rows from the first to row e; in this case, ":" can be omitted. |
|
e |
The ending row; if omitted, retrieve rows from row b to the last row; in this case, ":" cannot be omitted; if e is greater than the actual number of rows, use the actual number of rows. Retrieve rows backwards when e<0. |
|
p |
The password for accessing the Excel file. |
Option:
|
@t |
Export the first row in f as the field names; if not supplied, use _1, and _2,… as field names. When parameter b is supplied, it is treated as the header row. |
|
@c |
Return result as a cursor; support xlsx format only; in this case, parameter e should be greater than 0. |
|
@b |
Remove blank rows before and after the Excel data when reading them; will be ignored when @c option is present. |
|
@w |
Enable returning a sequence of sequences where members of sub-sequences are cell values; it cannot work with @t, @c and @b options. |
|
@p |
Work with @w to return a sequence of sequences; each sub-sequence is made up of column values. |
|
@s |
Enable returning a string delimited by CR/tab. |
|
@n |
Remove white spaces on both sides of a string; read an empty string as null. |
Return value:
Table sequence
Example:
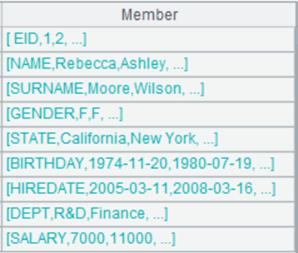
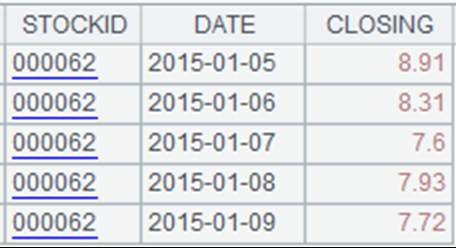
Read the whole xls file:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
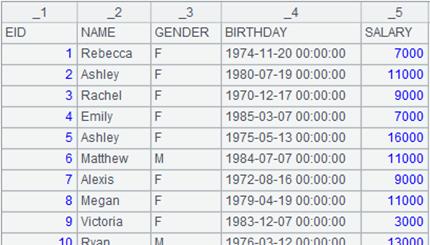
=file("emp1.xls").xlsimport() |
|
|
2 |
=file("password_abc.xls").xlsimport(;;"abc") |
Read an xls file encrypted with the password; the password for opening password_abc.xls is abc. |
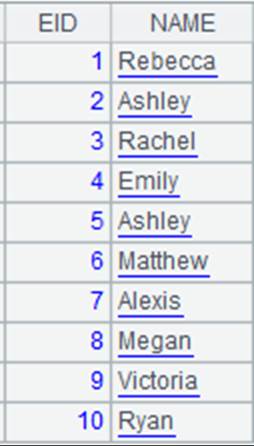
Read the first row of an xls file as the title and retrieve the specified fields:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=file("emp1.xls").xlsimport@t(NAME,GENDER;) |
Read NAME field and GENDER field.
|
|
2 |
=file("emp1.xls").xlsimport@t(#1,#2;) |
Read the first and the second fields from the xls file.
|
Read a multi-sheet xls file:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
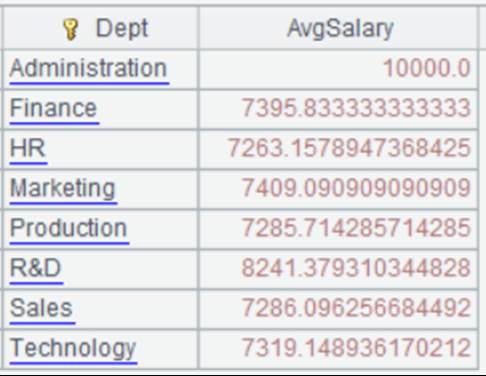
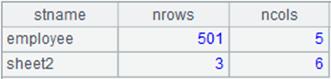
=file("emp2.xlsx").xlsimport@t(;"t1") |
emp2.xlsx contains two sheets, whose names are t1 and t2; Read data from sheet t1 through its name.
|
|
2 |
=file("emp2.xlsx").xlsimport@t(;2) |
Read data from the second sheet:
|
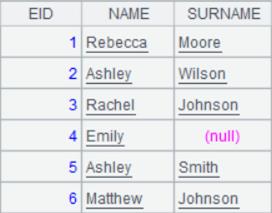
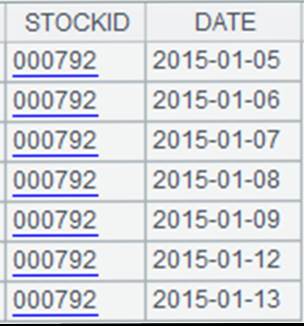
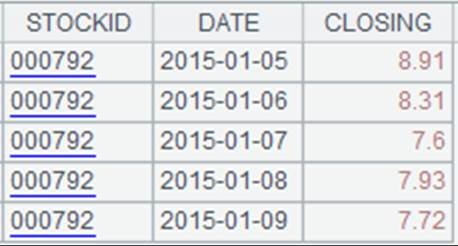
Specify the starting row and the ending row:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=file("emp2.xlsx").xlsimport(;2,3:6) |
Read rows from the third to the sixth in the second sheet of emp2.xlsx:
|
|
2 |
=file("emp2.xlsx").xlsimport@t(;2,3:6) |
As @t option works, read the 3rd row as the title:
|
|
3 |
=file("emp2.xlsx").xlsimport@t(;"t2",:6) |
As parameter b is absent, read the first row as the title and retrieve rows of the data from the first to the sixth; “:” should not be omitted.
|
|
4 |
=file("emp2.xlsx").xlsimport(;"t2",7:) |
As parameter e is absent, read rows of data from the seventh to the last; “:” can be omitted.
|
|
5 |
=file("emp2.xlsx").xlsimport(;"t2",3:-4) |
Read rows of data from the third to the fourth to the last.
|
Read content of the xlsx file and return it as a cursor:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=file("emp3.xlsx").xlsimport@c() |
Return a cursor. |
|
2 |
=A1.fetch() |
|
Remove blank rows before or after the Excel content during reading:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
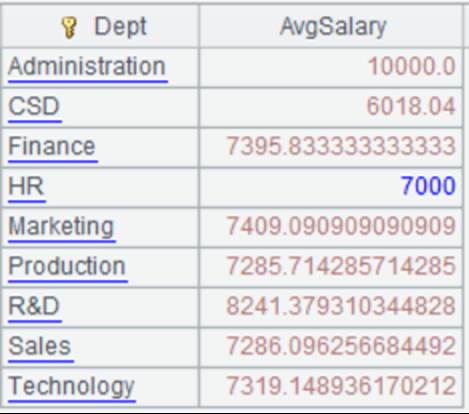
=file("emp4.xls") |
|
|
2 |
=A1.xlsimport@b() |
@b option works to remove blank rows before or after the Excel content during reading and use the first record as titles.
|
Return a sequence of sequences:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=file("emp1.xls").xlsimport@w() |
@w option works to return a sequence of sequences, where each row is a member of the sequence.
|
Retrun a sequence consisting of Excel columns:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=file("emp1.xls").xlsimport@pw() |
@wp options work to return a sequence made up of Excel columns, where each column is a member of the sequence.
|
Return a string delimited by /tab:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=file("emp1.xls").xlsimport@s() |
@s option works to return a string separated by CR/tab:
|
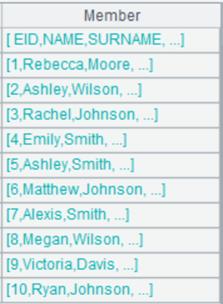
Remove white spaces at both ends of each string, and read empty strings as nulls:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
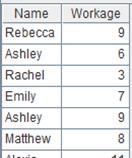
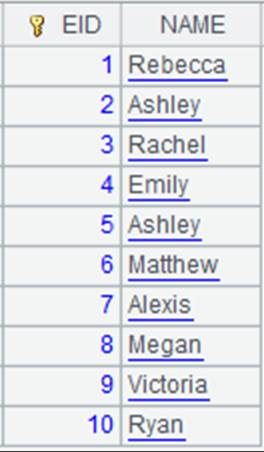
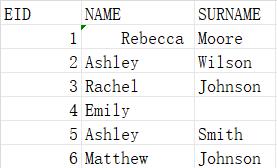
=file("emp5.xls") |
Below is content of emp5.xls:
|
|
2 |
=A1.xlsimport@nt() |
Remove white spaces at both ends of string “Rebecca”, and read an empty string as null:
|
Related functions:
xo.xlsimport()
Description:
Retrieve a table sequence from an Excel file object.
Syntax:
xo.xlsimport(Fi,..;s,b:e)
Note:
The function retrieves rows from row b to row e from the specified sheet s in Excel file f and returns them as a table sequence. Retrieve rows from the first to the last when both parameter b and parameter e are absent.
Parameter:
|
xo |
An Excel file object read in non-@w way. |
|
Fi |
Excel column name; retrieve all columns when omitted. Use the sequence number to locate a column when it is #. |
|
s |
Sheet name or sheet number; use the first sheet when omitted. |
|
b |
The starting row; if omitted, retrieve rows from the first to row e; in this case, ":" can be omitted. |
|
e |
The ending row; if omitted, retrieve rows from row b to the last; in this case, ":" cannot be omitted; if e is greater than the actual number of rows, use the actual number of rows. Retrieve rows backwards when e<0. It should be a positive integer when the Excel object is retrieved using @r. |
Option:
|
@t |
Export the first row of the Excel file as field names; if not supplied, use _1, and _2,… as field names. When parameter b is supplied, it is treated as the header row. |
|
@c |
Return the retrieved table sequence as a cursor; here the Excel file object must be read with @r option and parameter e should not be less than 0. |
|
@b |
Remove blank rows before and after the Excel data when reading content in; it becomes invalid when @c option is also present. |
|
@w |
Enable returning a sequence of sequences where members of sub-sequences are cell values; it cannot work with @t, @c and @b options. |
|
@p |
Must work with @w and return a sequence of sequences; each sub-sequence is made up of column values. |
|
@s |
Enable returning a string delimited by /tab. |
|
@n |
Remove white spaces on both sides of a string; read an empty string as null. |
Return value:
Table sequence
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=file("E1.xls").xlsopen() |
Read the E1.xls file and return it.
|
|
2 |
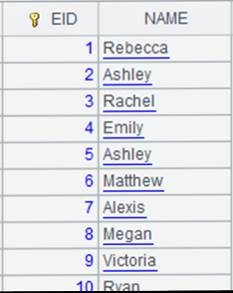
=A1.xlsimport() |
Read all data in the first sheet as there are no parameters:
|
|
3 |
=A1.xlsimport@t(ID,NAME;2) |
Retrieve columns whose names are ID and NAME on the second sheet, and make the first row as the header row.
|
|
4 |
=A1.xlsimport(;"employee",10:20) |
Retrieve data from row 10 to row 20 on the employee sheet.
|
|
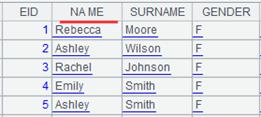
D:/excel/emp.xls |
Below is the content of emp.xls:
|
|
|
6 |
=file(A5).xlsopen().xlsimport@tb() |
Use @b option to remove blank rows before and after the data when
reading it. |
|
7 |
=file("E2.xlsx").xlsopen@r() |
Retrieve data from the Excel file in the @r way. |
|
8 |
=A7.xlsimport@c() |
Return Excel data as a cursor. |
|
9 |
=file("E3.xls").xlsopen().xlsimport@w(;2) |
Use @w option to return a sequence of sequences, whose members are Excel rows:
|
|
10 |
=file("E4.xls").xlsopen().xlsimport@wp() |
Use @wp options to return a sequence of sequences, whose members are Excel columns:
|
|
11 |
=file("E5.xls").xlsopen().xlsimport@s() |
@s option works to return a string delimited by CR/tab:
|
|
12 |
=file("E6.xls") |
Below is content of E6.xls:
|
|
13 |
=A12.xlsopen().xlsimport@n() |
Remove white spaces at both ends of string “Rebecca”, and read empty strings as nulls:
|