Logical table
A logical table is a virtual, single-field table without records. Being treated as an ordinary table, it is mainly used for defining the dimension hierarchy in scenarios where the corresponding physical tables are absent. For example, usually there isn’t a physical table corresponding to the time dimension, and the logical table can be created to do the same work.
For example, we can define the date hierarchy in demo.glmd through three logical tables – Day, Year and YearMonth:
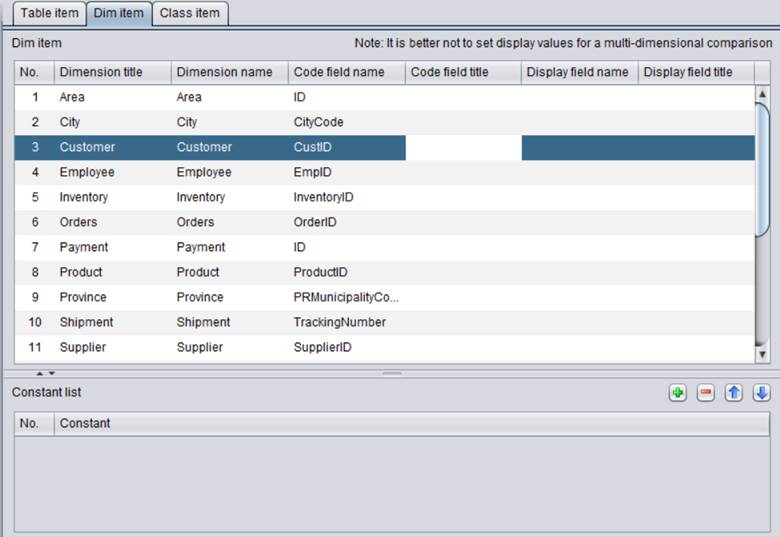
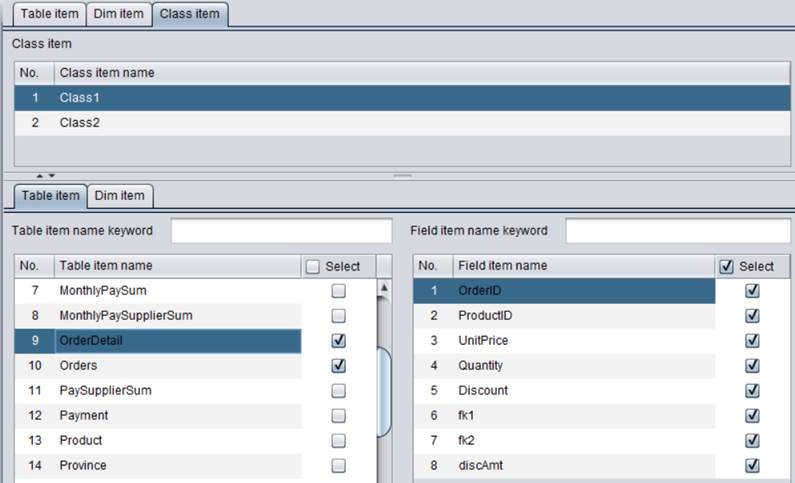
Note:
1. Here are system pre-defined level functions for date dimension:
|
year |
The year |
|
season |
The quarter |
|
month |
The month |
|
day |
The date |
|
week |
The day in a week; 1 represents Sunday |
|
yseason |
Quarter of the year |
|
ymonth |
Month of the year |
|
weeks |
Which week |
|
yweeks |
Which week in the current year |
|
sweeks |
Which week in the current quarter |
|
mweeks |
Which week in the current month |
2. A inter-level expression can be regarded as performing a computation from low to high in terms of granularity. For example, you can obtain the year from Day dimension, but cannot obtain the year from the day.
3. A target dimension can be obtained from different source dimensions. The “Year” dimension, for instance, can be obtained through aggregation either from the “Day” dimension or from the “YearMonth” dimension. Therefore, two inter-level expressions need to be defined for obtaining the “Year” dimension from Day table’s date value or from YearMonth table’s yearmonth value.
Next, you can directly use a defined date level function in the DQL query, as shown below:
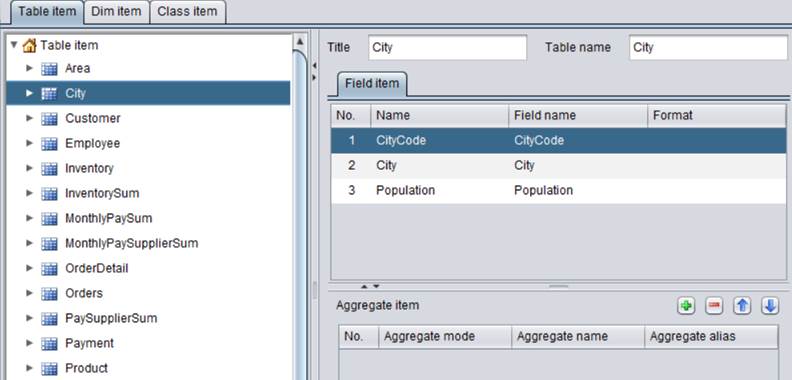
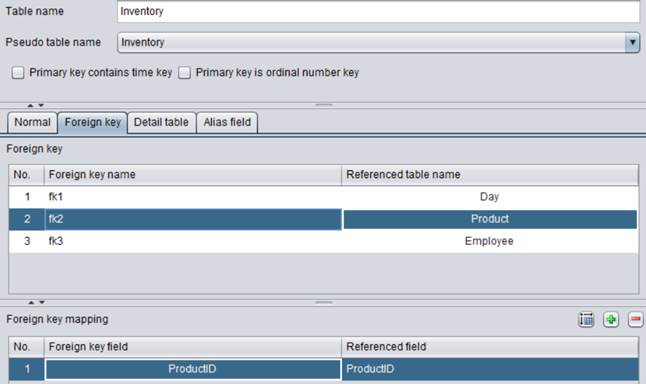
ReturnedPmt table’s Date field is date type. In the table’s foreign key definition, a foreign key association is established between the field and Day table’s Day field, as shown below:
This way you obtain year and month information of RDate through the DQL query. For instance, Date#Year obtains the year of RDate and Date#YearMonth gets year and month of RDate.
DQL: SELECT CustomerID,ID,Date,Date#YearMonth YearMonth,Date#Year Year,Amount,SellerID FROM ReturnedPmt
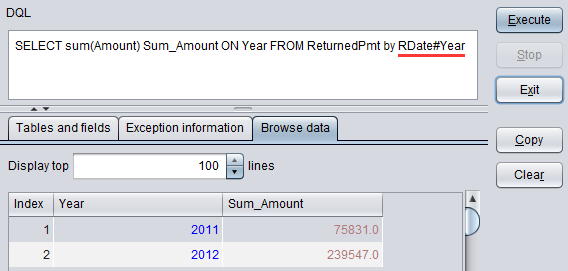
DQL: SELECT sum(Amount) Sum_Amount ON Year FROM ReturnedPmt by Date#Year
DQL: SELECT sum(Amount) Sum_Amount ON YearMonth FROM ReturnedPmt by Date#YearMonth