Deploying DQL Server
After esProc is installed, the application contains a set of metadata files in the format of composite tables (.ctx) and related DQL Server service. Users can deploy the DQL Server service within the esProc application or deploy their independent DQL Server. Below shows structure of the DQL Server directory:
DQL_Server_Root/ # DQL Server service root directory ( [esProc installation root directory]/esProc in the esProc product)
├── esproc-services/ # Multi-service instance master directory
│ ├── server.xml # Service configurations (including the server IP address, port number, name and other information)
│ ├── serverName 1/ # Directory of service instance 1
│ │ ├── service.xml # Configurations of service instance 1 (user information, metadata file path and other information)
│ │ └── conf/ # Special subdirectory for service instance 1
│ │ ├── *.glmd # Metadata file (.glmd)
│ │ ├── *. gdct # Dictionary file (.gdct; the extension is optional)
│ │ └── *.gvsb # Visual file(.gvsb; the extension is optional)
│ ├── serverName 2/ # Directory of service instance 2 (Same structure as instance 1)
│ └──… … # Multiple service instance can be configured
│ └── serverName n/ # Directory of service instance n (Same structure as instance 1)
├── log/ # Log file directory
Here are detailed explanations about the deployment and configurations of DQL Server.
To deploy DQL Server, follow these directions:
1. Load necessary jar files
No need to manually configure jar files when using DQL Server service in esProc products, and just skip this section.
Put the following jar files in a loadable directory at the startup of the DQL server. The path is [esProc installation root directory]/esProc/lib:
esproc-bin-***.jar DQL Server computing engine and JDBC driver jar file
esproc-ext-***.jar DQL Server computing engine and JDBC driver jar file
esproc-ent-***.jar DQL Server computing engine and JDBC driver jar file
json-20240303.jar For parsing JSON strings
lz4-1.3.0.jar For compressing ctx files
2. Deploying esproc-services directory
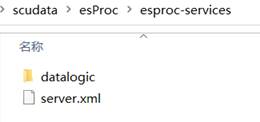
The esproc-services directory is DQL Server’s instance master directory, which contains multiple logical databases. Each logical database uses an independent directory, as the datalogic directory in the above screenshot shows. server.xml is for adding a to-be-used DQL Server logical database. Below shows a logical database directory:

1) service.xml is used to configure the logical database’s metadata file (*.glmd). It is located in service directory [esProc installation directory]\ esProc\esproc-services\.
2) The metadata file is generated by metadata design editor and stored in service directory \conf, under which there are also the dictionary file (*.gdct) and visual files (*.gvsb). The sample data files used in the metadata file are compressed in pseudo.zip under [esProc installation directory]\esProc\documents\en. The pseudo folder needs to be decompressed and placed under the file main directory for use.
Note:
Multiple DQL Server service instances are allowed within one process. Names of configuration files server.xml and service.xml must not be changed.
3. server.xml
Deploy server.xml in the [service root directory]/ esproc-services. Its contents are as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<SERVER host="127.0.0.1" port="3368" timeout="3000" log="true" raqsoftConfig="config\raqsoftConfig.xml" autoStart="false">
<SERVICE name="datalogic"/>
</SERVER>
These are properties of <SERVER/> tag:
host: DQL Server’s host IP address.
port: DQL Server’s listener port number, which is 3368 by default.
timeout: DQL Server longest client-side wait time, which is 3000 (unit:millisecond) by default. Wait again after timeout. This parameter affects the response time of closing DQL Server. The longer the client-side wait time, the less waste in CPU performance and the longer of response time for closing the server.
log: Specifies whether or not record the execution log. The default value is true. Log is stored in dql.txt_********.log under [installation directory]/esProc/log/.
raqsoftConfig: xml configuration file used to configure file main directory, serial number and other information. You can define your own name for the configuration file. The file path can be set as an absolute one or a relative one; the latter is relative to [service root directory].
autoStart: Specifies whether or not automatically start DQL service. Default is false.
<SERVICE/>: The list of to be started DQL Servers. Multiple servers can be configured under multiple <service/> nodes, where the service specified in each’s name property must be located in [service root directory]\ esproc-services. There may be multiple DQL Server service instance directories under esproc-services, but only the services listed under <service/> will be started.
name: DQL Server name, which must be the same as the corresponding folder in service instance directory.
Note: The nodes and properties highlighted in blue must be configured.
4. service.xml
Deploy service.xml in [service root directory]\esproc-services\service instance\. Its contents are as follows:
<SERVICE logicmetadata="demo.glmd" dictionary="demo.gdct">
<USERS>
<USER name="sa" password="sa" visibility="s1.gvsb"/>
<USER name="ww" password="ww"/>
<USER name="ee" password="ee"/>
</USERS>
</SERVICE>
Properties of <SERVER/> tag:
logicmetadata: Metadata file [.glmd] stored in [service root directory]\ esproc-services\service instance\conf.
dictionary:Dictionary file (.gdct); optional.
<USERS/> : DQL server user privilege settings. Configure multiple users under multiple <USER/> nodes.
<USER/> : DQL Server user connection information and visual file configurations.
name: User name, which is optional.
Password: User password, which is optional.
visibility:Visual file (.gvsb); optional.
Note: 1) The nodes and properties highlighted in blue must be configured.
2) If the xml file involves special characters, they need to be first escaped before being written to the file. For example, "&" needs to be written as "&".
5. Starting DQL Server
With an esProc product, you can start DQL Server through the startup file located in [esProc installation root directory]\esProc\bin:
Under Windows, double-click dqlserver.exe/startDQLSERVER.bat to start DQL Server:
Under Linux/Mac, you can start DQL Server through startDQLSERVER.sh or using the non-GUI method according to the following directions: get into [esProc installation root directory]\esProc\bin and execute command ./startDQLSERVER.sh -d to start DQL Server service; execute ./startDQLSERVER.sh -x to close DQL Server service.
To perform independent deployment, the execution command to start DQL Server should contain the following parameters:
javaw -Djava.ext.dirs=<JAR load path> -Dstart.home=<main path> com.esproc.dql.server.ServerConsole
Ø -Djava.ext.dirs: Specify the path for loading Java extension JAR files (replace <JAR load path> with the actual directory.
Ø -Dstart.home: Specify DQL Server’s service root directory (replace <main path> with the actual path).
Ø Startup class: com.esproc.dql.server.ServerConsole
Note: There must be the services subdirectory in the main directory specified in start.home.
A command example:
javaw -cp "D:\raqsoft\esProc\lib\*" -Dstart.home="D:\raqsoft\esProc" com.esproc.dql.server.ServerConsole
![]()
Execute the command and DQL Server window pops up. In the window click Start button to start the DQL service:
For convenience, you can turn the execution command into a startup file. For the script content, you can refer to startDQLSERVER.bat(/sh) located in [esProc installation root directory]/esProc/bin.
6. Connecting to DQL Server
Connect to DQL Server through JDBC after it is successfully started.
Connect to DQL Server according to the following directions:
JDBC:
Reference DQL Server JDBC’s driver jars (esproc-bin-***.jar, esproc-ext-***.jar and esproc-ent-***.jar) in the application when connecting DQL Server via JDBC.
Driver — com.esproc.dql.jdbc.DQLDriver
URL—jdbc: esproc:dql://[host]:[port],[host]:[port],.../[serviceName]?[&user={userName}]&[password={password}]
// Parameter:
[host]:[port] -> DQL Server’s IP address and port number; there can be multiple sets of them but make sure that except for the IP and port, other contents should maintain the same. Connect to the directly next one when the current service cannot be connected until the Server is connected successfully.
[serviceName] -> Name of the to-be-connected DQL Server
[userName]/[password] -> User name and password of DQL Server service